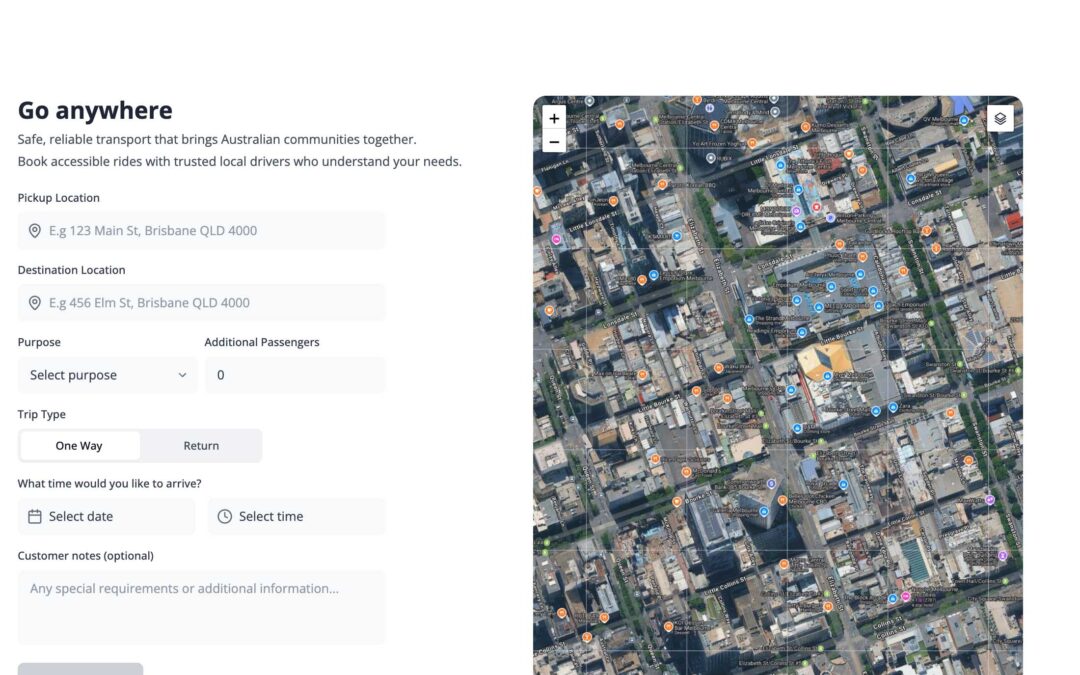
Technology within the Transport space is evolving rapidly. With new technology comes new words to describe it. Some of these have obvious definitions, whereas others are a little less straightforward. We’ve compiled the most common terms used in the transport tech space.
Table of Contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field, encompassing any system that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. AI has many applications in Transport Technology, and we’ll see it being increasingly adopted over time.
Application programming interface (API)
An API is a set of rules and tools that allows different software applications to communicate with each other. An API on a website provides a list of operations you can perform and instructions on how to perform them. You can request specific things through an API, and it gives you the response or data you need.
Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) integrates digital information with the user’s environment in real time. This usually involves someone using a device such as a smartphone or AR glasses. The result is a feeling of being in the real world, but with digital elements layered on top of it.
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs)
Autonomous vehicles (AVs), also known as self-driving cars, are vehicles equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence to navigate and operate without human intervention. These vehicles use algorithms and machine learning to interpret data from their environment and make driving decisions.
Biometric data
Biometric data are our unique biological characteristics such as fingerprints, patterns on our eyes and heart rate. Biometric data is collected frequently in our day-to-day lives, such as through our stored fingerprints or facial features that we use to unlock our smartphones and other devices.
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is an AI-powered machine developed by OpenAI. It is a computer program that you can write (or speak) questions to, and it will reply in a way that mimics a typical “human” conversation. It uses a vast amount of data and Large Language Models (LLM)to answer your questions with relevant responses.
Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles are equipped with internet access and communication capabilities that allow them to share data with other vehicles, infrastructure, and central systems. This connectivity enables various applications, including traffic management, safety alerts, and infotainment services, improving overall transportation efficiency and safety.
Data Analytics
Data analytics refers to the analysis of large sets of data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. In home and residential care, data analytics can help optimise workflows, predict patient needs, and improve decision-making processes.
Data Centres
Specialised facilities designed to house, manage, and process large amounts of data. They provide the necessary infrastructure, including servers, storage systems, networking equipment, and cooling systems, to ensure the reliable and efficient operation of data-intensive applications. In the context of transportation technology, data centres support the processing and storage of vast amounts of data generated by connected vehicles, smart infrastructure, and various digital services, enabling real-time analytics, decision-making, and communication.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that involves training artificial neural networks with multiple “deep” layers to learn from large amounts of data. It mimics the way the human brain processes information, allowing computers to recognise patterns, make decisions, and perform complex tasks.
Digital Twins
A virtual representation of a physical object, system, or process that is used to simulate, analyse, and optimise real-world counterparts. In transportation, digital twins can model vehicles, infrastructure, or entire transportation networks to monitor performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve operational efficiency. By leveraging real-time data and advanced simulations, digital twins help in making informed decisions and enhancing the reliability and safety of transportation systems.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI)
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure (EVCI) refers to the network of charging stations and related equipment that support the recharging of electric vehicles. EVCI includes various types of chargers, such as Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast chargers, as well as the necessary electrical and communication systems to manage charging operations.
Electrification
Electrification refers to the process of replacing technologies that use fossil fuels with technologies that use electricity as a power source. In transportation, this often involves transitioning from gasoline or diesel-powered vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs), which are more environmentally friendly and often more efficient.
Generative AI (GenAI)
GenAI refers to AI systems (like ChatGPT) that can create new content, such as text, images, or music, based on patterns learned from existing data. Unlike traditional AI systems that are primarily used for classification, prediction, or optimisation tasks, GenAI focuses on generating novel outputs.
Geofencing
Geofencing is a technology that creates virtual boundaries around a specific geographic area using GPS or RFID technology. When a vehicle enters or exits a geofenced area, the system can trigger predefined actions such as sending alerts, adjusting speed limits, or controlling access. Geofencing is used in fleet management, autonomous vehicle operations, and smart city applications.
Hallucination
Hallucination (in the context of LLM) refers to when a LLM, generates responses that are unrelated to the input or deviate significantly from the context provided. This may result in incorrect, irrelevant, or even completely fictional answers.
In-Vehicle Monitoring System (IVMS)
Technology used to monitor and record the activities and behaviors of a vehicle and its driver. This system collects data on various parameters such as speed, location, fuel consumption, and driver behavior. It helps improve safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
Large Language Models (LLMs) is a type of AI specifically designed to understand and generate human-like text based on extensive training on a large dataset. LLMs can summarise, extract and query information from new documents. There are thousands of ways you can use it, with more evolving every day.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field of AI that focuses on the interaction between computers and humans through natural language. The goal of NLP is to enable computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language in a way that is both meaningful and useful.
Predictive Modelling
Predictive Modelling is a process used in ML to create a model that predicts future outcomes based on historical data. This involves various algorithms and techniques, including regression, classification, and time series analysis.
Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering refers to using specific cues or language that elicits a desired outcome from an LLM. For example, any time you ask ChatGPT specific questions with the intention of seeking a certain answer, you are employing the principles of prompt engineering. Prompt engineering incorporates everything from superficial, simple prompts, to complicated and detailed prompts.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
In Robotic Process Automation (RPA), software bots are used to automate repetitive tasks. This automation can be for administrative tasks, data entry, financial transactions, and more.
Smart Highways
Smart Highways are roads equipped with advanced technologies to improve the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of transportation. These technologies include sensors, IoT devices, and communication systems that provide real-time data on traffic conditions, weather, and road hazards. Smart highways can also include features like dynamic lane management, adaptive lighting, and wireless charging for electric vehicles.
Smart Home
Smart Home tech has been widely available for many years, and its adoption will likely only increase. A smart home is a home equipped with devices and appliances that are connected to a central network. These can be controlled remotely or automated to perform tasks autonomously. Examples of these devices are lighting systems, security cameras, door locks, and kitchen appliances, among other things.
Smart Tech
Refers to devices and systems that are interconnected and can communicate with each other to perform automated tasks and provide enhanced services. In transportation, smart tech includes connected vehicles, traffic management systems, and infrastructure that can adapt to changing conditions. These technologies aim to improve efficiency, safety, and convenience.
Telematics
Telematics is the integration of telecommunications and information technology to provide services such as vehicle tracking, navigation, and remote diagnostics. Telematics systems collect and transmit data about a vehicle’s location, performance, and usage, helping fleet managers optimize operations and improve maintenance.
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication
Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication is a technology that enables vehicles to communicate with each other and with infrastructure such as traffic lights and road signs. V2X aims to improve traffic efficiency, safety, and the overall driving experience by providing real-time information and enabling coordinated actions among vehicles.
Virtual Reality
Virtual Reality (VR) immerses users in computer-generated environments, often experienced through headsets or goggles. This is different from augmented reality in that augmented reality overlays digital content into the real world, whereas virtual reality creates a fully immersive, fictional world.